Introduction
In addition to support for sending email, Laravel provides support for sending notifications across a variety of delivery channels, including email, SMS (via Vonage, formerly known as Nexmo), and Slack. In addition, a variety of community built notification channels have been created to send notifications over dozens of different channels! Notifications may also be stored in a database so they may be displayed in your web interface.
Typically, notifications should be short, informational messages that notify users of something that occurred in your application. For example, if you are writing a billing application, you might send an "Invoice Paid" notification to your users via the email and SMS channels.
Generating Notifications
In Laravel, each notification is represented by a single
class that is typically stored in the
app/Notifications directory. Don't worry if
you don't see this directory in your application - it
will be created for you when you run the
make:notification Artisan command:
php artisan make:notification InvoicePaid
This command will place a fresh notification class in
your app/Notifications directory. Each
notification class contains a via method
and a variable number of message building methods, such
as toMail or toDatabase, that
convert the notification to a message tailored for that
particular channel.
Sending Notifications
Using the Notifiable Trait
Notifications may be sent in two ways: using the
notify method of the
Notifiable trait or using the
Notification facade. The
Notifiable trait is included on your
application's App\Models\User model by
default:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable;
class User extends Authenticatable
{
use Notifiable;
}
The notify method that is provided by this
trait expects to receive a notification instance:
use App\Notifications\InvoicePaid;
$user->notify(new InvoicePaid($invoice));
Note:
Remember, you may use theNotifiabletrait on any of your models. You are not limited to only including it on yourUsermodel.
Using the Notification Facade
Alternatively, you may send notifications via the
Notification facade. This approach is
useful when you need to send a notification to multiple
notifiable entities such as a collection of users. To
send notifications using the facade, pass all of the
notifiable entities and the notification instance to the
send method:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Notification;
Notification::send($users, new InvoicePaid($invoice));
You can also send notifications immediately using the
sendNow method. This method will send the
notification immediately even if the notification
implements the ShouldQueue interface:
Notification::sendNow($developers, new DeploymentCompleted($deployment));
Specifying Delivery Channels
Every notification class has a via method
that determines on which channels the notification will
be delivered. Notifications may be sent on the
mail, database,
broadcast, vonage, and
slack channels.
Note:
If you would like to use other delivery channels such as Telegram or Pusher, check out the community driven Laravel Notification Channels website.
The via method receives a
$notifiable instance, which will be an
instance of the class to which the notification is being
sent. You may use $notifiable to determine
which channels the notification should be delivered
on:
/**
* Get the notification's delivery channels.
*
* @return array<int, string>
*/
public function via(object $notifiable): array
{
return $notifiable->prefers_sms ? ['vonage'] : ['mail', 'database'];
}
Queueing Notifications
Warning!
Before queueing notifications you should configure your queue and start a worker.
Sending notifications can take time, especially if the
channel needs to make an external API call to deliver
the notification. To speed up your application's
response time, let your notification be queued by adding
the ShouldQueue interface and
Queueable trait to your class. The
interface and trait are already imported for all
notifications generated using the
make:notification command, so you may
immediately add them to your notification class:
<?php
namespace App\Notifications;
use Illuminate\Bus\Queueable;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\ShouldQueue;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
class InvoicePaid extends Notification implements ShouldQueue
{
use Queueable;
// ...
}
Once the ShouldQueue interface has been
added to your notification, you may send the
notification like normal. Laravel will detect the
ShouldQueue interface on the class and
automatically queue the delivery of the
notification:
$user->notify(new InvoicePaid($invoice));
When queueing notifications, a queued job will be created for each recipient and channel combination. For example, six jobs will be dispatched to the queue if your notification has three recipients and two channels.
Delaying Notifications
If you would like to delay the delivery of the
notification, you may chain the delay
method onto your notification instantiation:
$delay = now()->addMinutes(10);
$user->notify((new InvoicePaid($invoice))->delay($delay));
Delaying Notifications per Channel
You may pass an array to the delay method to
specify the delay amount for specific channels:
$user->notify((new InvoicePaid($invoice))->delay([
'mail' => now()->addMinutes(5),
'sms' => now()->addMinutes(10),
]));
Alternatively, you may define a withDelay
method on the notification class itself. The
withDelay method should return an array of
channel names and delay values:
/**
* Determine the notification's delivery delay.
*
* @return array<string, \Illuminate\Support\Carbon>
*/
public function withDelay(object $notifiable): array
{
return [
'mail' => now()->addMinutes(5),
'sms' => now()->addMinutes(10),
];
}
Customizing the Notification Queue Connection
By default, queued notifications will be queued using
your application's default queue connection. If you
would like to specify a different connection that should
be used for a particular notification, you may call the
onConnection method from your
notification's constructor:
<?php
namespace App\Notifications;
use Illuminate\Bus\Queueable;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\ShouldQueue;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
class InvoicePaid extends Notification implements ShouldQueue
{
use Queueable;
/**
* Create a new notification instance.
*/
public function __construct()
{
$this->onConnection('redis');
}
}
Or, if you would like to specify a specific queue
connection that should be used for each notification
channel supported by the notification, you may define a
viaConnections method on your notification.
This method should return an array of channel name /
queue connection name pairs:
/**
* Determine which connections should be used for each notification channel.
*
* @return array<string, string>
*/
public function viaConnections(): array
{
return [
'mail' => 'redis',
'database' => 'sync',
];
}
Customizing Notification Channel Queues
If you would like to specify a specific queue that should
be used for each notification channel supported by the
notification, you may define a viaQueues
method on your notification. This method should return
an array of channel name / queue name pairs:
/**
* Determine which queues should be used for each notification channel.
*
* @return array<string, string>
*/
public function viaQueues(): array
{
return [
'mail' => 'mail-queue',
'slack' => 'slack-queue',
];
}
Queued Notifications and Database Transactions
When queued notifications are dispatched within database transactions, they may be processed by the queue before the database transaction has committed. When this happens, any updates you have made to models or database records during the database transaction may not yet be reflected in the database. In addition, any models or database records created within the transaction may not exist in the database. If your notification depends on these models, unexpected errors can occur when the job that sends the queued notification is processed.
If your queue connection's after_commit
configuration option is set to false, you
may still indicate that a particular queued notification
should be dispatched after all open database
transactions have been committed by calling the
afterCommit method when sending the
notification:
use App\Notifications\InvoicePaid;
$user->notify((new InvoicePaid($invoice))->afterCommit());
Alternatively, you may call the afterCommit
method from your notification's constructor:
<?php
namespace App\Notifications;
use Illuminate\Bus\Queueable;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\ShouldQueue;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
class InvoicePaid extends Notification implements ShouldQueue
{
use Queueable;
/**
* Create a new notification instance.
*/
public function __construct()
{
$this->afterCommit();
}
}
Note:
To learn more about working around these issues, please review the documentation regarding queued jobs and database transactions.
Determining if a Queued Notification Should Be Sent
After a queued notification has been dispatched for the queue for background processing, it will typically be accepted by a queue worker and sent to its intended recipient.
However, if you would like to make the final
determination on whether the queued notification should
be sent after it is being processed by a queue worker,
you may define a shouldSend method on the
notification class. If this method returns
false, the notification will not be
sent:
/**
* Determine if the notification should be sent.
*/
public function shouldSend(object $notifiable, string $channel): bool
{
return $this->invoice->isPaid();
}
On-Demand Notifications
Sometimes you may need to send a notification to someone
who is not stored as a "user" of your
application. Using the Notification
facade's route method, you may specify
ad-hoc notification routing information before sending
the notification:
use Illuminate\Broadcasting\Channel;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Notification;
Notification::route('mail', 'taylor@example.com')
->route('vonage', '5555555555')
->route('slack', '#slack-channel')
->route('broadcast', [new Channel('channel-name')])
->notify(new InvoicePaid($invoice));
If you would like to provide the recipient's name when
sending an on-demand notification to the
mail route, you may provide an array that
contains the email address as the key and the name as
the value of the first element in the array:
Notification::route('mail', [
'barrett@example.com' => 'Barrett Blair',
])->notify(new InvoicePaid($invoice));
Using the routes method, you may provide
ad-hoc routing information for multiple notification
channels at once:
Notification::routes([
'mail' => ['barrett@example.com' => 'Barrett Blair'],
'vonage' => '5555555555',
])->notify(new InvoicePaid($invoice));
Mail Notifications
Formatting Mail Messages
If a notification supports being sent as an email, you
should define a toMail method on the
notification class. This method will receive a
$notifiable entity and should return an
Illuminate\Notifications\Messages\MailMessage
instance.
The MailMessage class contains a few simple
methods to help you build transactional email messages.
Mail messages may contain lines of text as well as a
"call to action". Let's take a look at an
example toMail method:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
$url = url('/invoice/'.$this->invoice->id);
return (new MailMessage)
->greeting('Hello!')
->line('One of your invoices has been paid!')
->lineIf($this->amount > 0, "Amount paid: {$this->amount}")
->action('View Invoice', $url)
->line('Thank you for using our application!');
}
Note:
Note we are using$this->invoice->idin ourtoMailmethod. You may pass any data your notification needs to generate its message into the notification's constructor.
In this example, we register a greeting, a line of text,
a call to action, and then another line of text. These
methods provided by the MailMessage object
make it simple and fast to format small transactional
emails. The mail channel will then translate the message
components into a beautiful, responsive HTML email
template with a plain-text counterpart. Here is an
example of an email generated by the mail
channel:
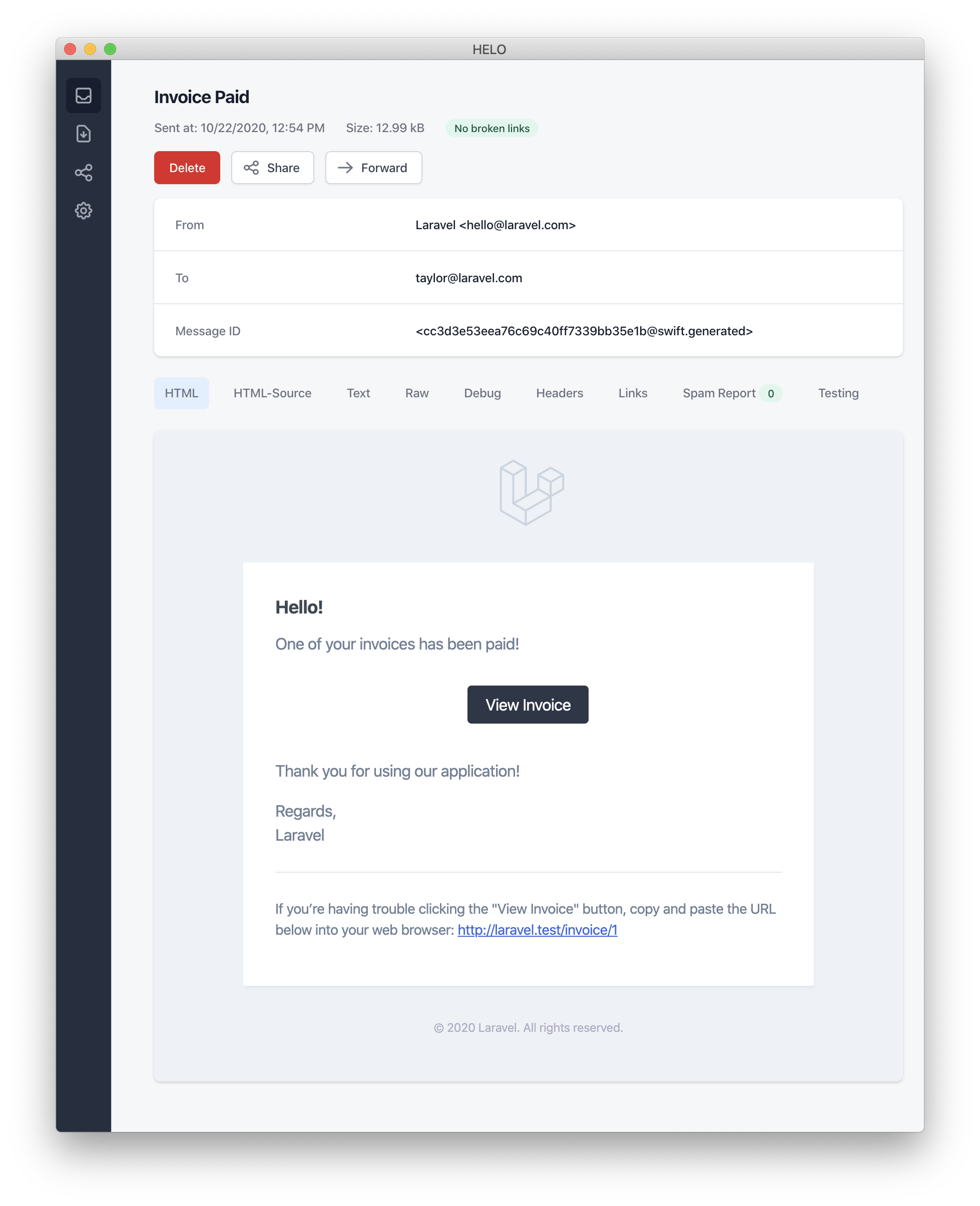
Note:
When sending mail notifications, be sure to set thenameconfiguration option in yourconfig/app.phpconfiguration file. This value will be used in the header and footer of your mail notification messages.
Error Messages
Some notifications inform users of errors, such as a
failed invoice payment. You may indicate that a mail
message is regarding an error by calling the
error method when building your message.
When using the error method on a mail
message, the call to action button will be red instead
of black:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->error()
->subject('Invoice Payment Failed')
->line('...');
}
Other Mail Notification Formatting Options
Instead of defining the "lines" of text in the
notification class, you may use the view
method to specify a custom template that should be used
to render the notification email:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)->view(
'mail.invoice.paid', ['invoice' => $this->invoice]
);
}
You may specify a plain-text view for the mail message by
passing the view name as the second element of an array
that is given to the view method:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)->view(
['mail.invoice.paid', 'mail.invoice.paid-text'],
['invoice' => $this->invoice]
);
}
Or, if your message only has a plain-text view, you may
utilize the text method:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)->text(
'mail.invoice.paid-text', ['invoice' => $this->invoice]
);
}
Customizing the Sender
By default, the email's sender / from address is defined
in the config/mail.php configuration file.
However, you may specify the from address for a specific
notification using the from method:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->from('barrett@example.com', 'Barrett Blair')
->line('...');
}
Customizing the Recipient
When sending notifications via the mail
channel, the notification system will automatically look
for an email property on your notifiable
entity. You may customize which email address is used to
deliver the notification by defining a
routeNotificationForMail method on the
notifiable entity:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
class User extends Authenticatable
{
use Notifiable;
/**
* Route notifications for the mail channel.
*
* @return array<string, string>|string
*/
public function routeNotificationForMail(Notification $notification): array|string
{
// Return email address only...
return $this->email_address;
// Return email address and name...
return [$this->email_address => $this->name];
}
}
Customizing the Subject
By default, the email's subject is the class name of the
notification formatted to "Title Case". So, if
your notification class is named
InvoicePaid, the email's subject will be
Invoice Paid. If you would like to specify
a different subject for the message, you may call the
subject method when building your
message:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->subject('Notification Subject')
->line('...');
}
Customizing the Mailer
By default, the email notification will be sent using the
default mailer defined in the
config/mail.php configuration file.
However, you may specify a different mailer at runtime
by calling the mailer method when building
your message:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->mailer('postmark')
->line('...');
}
Customizing the Templates
You can modify the HTML and plain-text template used by
mail notifications by publishing the notification
package's resources. After running this command, the
mail notification templates will be located in the
resources/views/vendor/notifications
directory:
php artisan vendor:publish --tag=laravel-notifications
Attachments
To add attachments to an email notification, use the
attach method while building your message.
The attach method accepts the absolute path
to the file as its first argument:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->greeting('Hello!')
->attach('/path/to/file');
}
Note:
Theattachmethod offered by notification mail messages also accepts attachable objects. Please consult the comprehensive attachable object documentation to learn more.
When attaching files to a message, you may also specify
the display name and / or MIME type by passing an
array as the second argument to the
attach method:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->greeting('Hello!')
->attach('/path/to/file', [
'as' => 'name.pdf',
'mime' => 'application/pdf',
]);
}
Unlike attaching files in mailable objects, you may not
attach a file directly from a storage disk using
attachFromStorage. You should rather use
the attach method with an absolute path to
the file on the storage disk. Alternatively, you could
return a mailable
from the toMail method:
use App\Mail\InvoicePaid as InvoicePaidMailable;
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): Mailable
{
return (new InvoicePaidMailable($this->invoice))
->to($notifiable->email)
->attachFromStorage('/path/to/file');
}
When necessary, multiple files may be attached to a
message using the attachMany method:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->greeting('Hello!')
->attachMany([
'/path/to/forge.svg',
'/path/to/vapor.svg' => [
'as' => 'Logo.svg',
'mime' => 'image/svg xml',
],
]);
}
Raw Data Attachments
The attachData method may be used to attach
a raw string of bytes as an attachment. When calling the
attachData method, you should provide the
filename that should be assigned to the attachment:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->greeting('Hello!')
->attachData($this->pdf, 'name.pdf', [
'mime' => 'application/pdf',
]);
}
Adding Tags and Metadata
Some third-party email providers such as Mailgun and
Postmark support message "tags" and
"metadata", which may be used to group and
track emails sent by your application. You may add tags
and metadata to an email message via the
tag and metadata methods:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->greeting('Comment Upvoted!')
->tag('upvote')
->metadata('comment_id', $this->comment->id);
}
If your application is using the Mailgun driver, you may consult Mailgun's documentation for more information on tags and metadata. Likewise, the Postmark documentation may also be consulted for more information on their support for tags and metadata.
If your application is using Amazon SES to send emails,
you should use the metadata method to
attach SES
"tags" to the message.
Customizing the Symfony Message
The withSymfonyMessage method of the
MailMessage class allows you to register a
closure which will be invoked with the Symfony Message
instance before sending the message. This gives you an
opportunity to deeply customize the message before it is
delivered:
use Symfony\Component\Mime\Email;
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->withSymfonyMessage(function (Email $message) {
$message->getHeaders()->addTextHeader(
'Custom-Header', 'Header Value'
);
});
}
Using Mailables
If needed, you may return a full mailable object from your
notification's toMail method. When
returning a Mailable instead of a
MailMessage, you will need to specify the
message recipient using the mailable object's
to method:
use App\Mail\InvoicePaid as InvoicePaidMailable;
use Illuminate\Mail\Mailable;
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): Mailable
{
return (new InvoicePaidMailable($this->invoice))
->to($notifiable->email);
}
Mailables and On-Demand Notifications
If you are sending an on-demand
notification, the $notifiable
instance given to the toMail method will be
an instance of
Illuminate\Notifications\AnonymousNotifiable,
which offers a routeNotificationFor method
that may be used to retrieve the email address the
on-demand notification should be sent to:
use App\Mail\InvoicePaid as InvoicePaidMailable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\AnonymousNotifiable;
use Illuminate\Mail\Mailable;
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): Mailable
{
$address = $notifiable instanceof AnonymousNotifiable
? $notifiable->routeNotificationFor('mail')
: $notifiable->email;
return (new InvoicePaidMailable($this->invoice))
->to($address);
}
Previewing Mail Notifications
When designing a mail notification template, it is
convenient to quickly preview the rendered mail message
in your browser like a typical Blade template. For this
reason, Laravel allows you to return any mail message
generated by a mail notification directly from a route
closure or controller. When a MailMessage
is returned, it will be rendered and displayed in the
browser, allowing you to quickly preview its design
without needing to send it to an actual email
address:
use App\Models\Invoice;
use App\Notifications\InvoicePaid;
Route::get('/notification', function () {
$invoice = Invoice::find(1);
return (new InvoicePaid($invoice))
->toMail($invoice->user);
});
Markdown Mail Notifications
Markdown mail notifications allow you to take advantage of the pre-built templates of mail notifications, while giving you more freedom to write longer, customized messages. Since the messages are written in Markdown, Laravel is able to render beautiful, responsive HTML templates for the messages while also automatically generating a plain-text counterpart.
Generating the Message
To generate a notification with a corresponding Markdown
template, you may use the --markdown option
of the make:notification Artisan
command:
php artisan make:notification InvoicePaid --markdown=mail.invoice.paid
Like all other mail notifications, notifications that use
Markdown templates should define a toMail
method on their notification class. However, instead of
using the line and action
methods to construct the notification, use the
markdown method to specify the name of the
Markdown template that should be used. An array of data
you wish to make available to the template may be passed
as the method's second argument:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
$url = url('/invoice/'.$this->invoice->id);
return (new MailMessage)
->subject('Invoice Paid')
->markdown('mail.invoice.paid', ['url' => $url]);
}
Writing the Message
Markdown mail notifications use a combination of Blade components and Markdown syntax which allow you to easily construct notifications while leveraging Laravel's pre-crafted notification components:
<x-mail::message>
# Invoice Paid
Your invoice has been paid!
<x-mail::button :url="$url">
View Invoice
</x-mail::button>
Thanks,<br>
{{ config('app.name') }}
</x-mail::message>
Button Component
The button component renders a centered button link. The
component accepts two arguments, a url and
an optional color. Supported colors are
primary, green, and
red. You may add as many button components
to a notification as you wish:
<x-mail::button :url="$url" color="green">
View Invoice
</x-mail::button>
Panel Component
The panel component renders the given block of text in a panel that has a slightly different background color than the rest of the notification. This allows you to draw attention to a given block of text:
<x-mail::panel>
This is the panel content.
</x-mail::panel>
Table Component
The table component allows you to transform a Markdown table into an HTML table. The component accepts the Markdown table as its content. Table column alignment is supported using the default Markdown table alignment syntax:
<x-mail::table>
| Laravel | Table | Example |
| ------------- |:-------------:| --------:|
| Col 2 is | Centered | $10 |
| Col 3 is | Right-Aligned | $20 |
</x-mail::table>
Customizing the Components
You may export all of the Markdown notification
components to your own application for customization. To
export the components, use the
vendor:publish Artisan command to publish
the laravel-mail asset tag:
php artisan vendor:publish --tag=laravel-mail
This command will publish the Markdown mail components to
the resources/views/vendor/mail directory.
The mail directory will contain an
html and a text directory,
each containing their respective representations of
every available component. You are free to customize
these components however you like.
Customizing the CSS
After exporting the components, the
resources/views/vendor/mail/html/themes
directory will contain a default.css file.
You may customize the CSS in this file and your styles
will automatically be in-lined within the HTML
representations of your Markdown notifications.
If you would like to build an entirely new theme for
Laravel's Markdown components, you may place a CSS file
within the html/themes directory. After
naming and saving your CSS file, update the
theme option of the mail
configuration file to match the name of your new
theme.
To customize the theme for an individual notification,
you may call the theme method while
building the notification's mail message. The
theme method accepts the name of the theme
that should be used when sending the notification:
/**
* Get the mail representation of the notification.
*/
public function toMail(object $notifiable): MailMessage
{
return (new MailMessage)
->theme('invoice')
->subject('Invoice Paid')
->markdown('mail.invoice.paid', ['url' => $url]);
}
Database Notifications
Prerequisites
The database notification channel stores the
notification information in a database table. This table
will contain information such as the notification type
as well as a JSON data structure that describes the
notification.
You can query the table to display the notifications in
your application's user interface. But, before you can
do that, you will need to create a database table to
hold your notifications. You may use the
notifications:table command to generate a
migration with the proper
table schema:
php artisan notifications:table
php artisan migrate
Note:
If your notifiable models are using UUID or ULID primary keys, you should replace themorphsmethod withuuidMorphsorulidMorphsin the notification table migration.
Formatting Database Notifications
If a notification supports being stored in a database
table, you should define a toDatabase or
toArray method on the notification class.
This method will receive a $notifiable
entity and should return a plain PHP array. The returned
array will be encoded as JSON and stored in the
data column of your
notifications table. Let's take a look at
an example toArray method:
/**
* Get the array representation of the notification.
*
* @return array<string, mixed>
*/
public function toArray(object $notifiable): array
{
return [
'invoice_id' => $this->invoice->id,
'amount' => $this->invoice->amount,
];
}
When the notification is stored in your application's
database, the type column will be populated
with the notification's class name. However, you may
customize this behavior by defining a
databaseType method on your notification
class:
/**
* Get the notification's database type.
*
* @return string
*/
public function databaseType(object $notifiable): string
{
return 'invoice-paid';
}
toDatabase vs. toArray
The toArray method is also used by the
broadcast channel to determine which data
to broadcast to your JavaScript powered frontend. If you
would like to have two different array representations
for the database and broadcast
channels, you should define a toDatabase
method instead of a toArray method.
Accessing the Notifications
Once notifications are stored in the database, you need a
convenient way to access them from your notifiable
entities. The
Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable trait,
which is included on Laravel's default
App\Models\User model, includes a
notifications Eloquent
relationship that returns the notifications for
the entity. To fetch notifications, you may access this
method like any other Eloquent relationship. By default,
notifications will be sorted by the
created_at timestamp with the most recent
notifications at the beginning of the collection:
$user = App\Models\User::find(1);
foreach ($user->notifications as $notification) {
echo $notification->type;
}
If you want to retrieve only the "unread"
notifications, you may use the
unreadNotifications relationship. Again,
these notifications will be sorted by the
created_at timestamp with the most recent
notifications at the beginning of the collection:
$user = App\Models\User::find(1);
foreach ($user->unreadNotifications as $notification) {
echo $notification->type;
}
Note:
To access your notifications from your JavaScript client, you should define a notification controller for your application which returns the notifications for a notifiable entity, such as the current user. You may then make an HTTP request to that controller's URL from your JavaScript client.
Marking Notifications as Read
Typically, you will want to mark a notification as
"read" when a user views it. The
Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable trait
provides a markAsRead method, which updates
the read_at column on the notification's
database record:
$user = App\Models\User::find(1);
foreach ($user->unreadNotifications as $notification) {
$notification->markAsRead();
}
However, instead of looping through each notification,
you may use the markAsRead method directly
on a collection of notifications:
$user->unreadNotifications->markAsRead();
You may also use a mass-update query to mark all of the notifications as read without retrieving them from the database:
$user = App\Models\User::find(1);
$user->unreadNotifications()->update(['read_at' => now()]);
You may delete the notifications to remove
them from the table entirely:
$user->notifications()->delete();
Broadcast Notifications
Prerequisites
Before broadcasting notifications, you should configure and be familiar with Laravel's event broadcasting services. Event broadcasting provides a way to react to server-side Laravel events from your JavaScript powered frontend.
Formatting Broadcast Notifications
The broadcast channel broadcasts
notifications using Laravel's event broadcasting
services, allowing your JavaScript powered frontend to
catch notifications in realtime. If a notification
supports broadcasting, you can define a
toBroadcast method on the notification
class. This method will receive a
$notifiable entity and should return a
BroadcastMessage instance. If the
toBroadcast method does not exist, the
toArray method will be used to gather the
data that should be broadcast. The returned data will be
encoded as JSON and broadcast to your JavaScript powered
frontend. Let's take a look at an example
toBroadcast method:
use Illuminate\Notifications\Messages\BroadcastMessage;
/**
* Get the broadcastable representation of the notification.
*/
public function toBroadcast(object $notifiable): BroadcastMessage
{
return new BroadcastMessage([
'invoice_id' => $this->invoice->id,
'amount' => $this->invoice->amount,
]);
}
Broadcast Queue Configuration
All broadcast notifications are queued for broadcasting.
If you would like to configure the queue connection or
queue name that is used to queue the broadcast
operation, you may use the onConnection and
onQueue methods of the
BroadcastMessage:
return (new BroadcastMessage($data))
->onConnection('sqs')
->onQueue('broadcasts');
Customizing the Notification Type
In addition to the data you specify, all broadcast
notifications also have a type field
containing the full class name of the notification. If
you would like to customize the notification
type, you may define a
broadcastType method on the notification
class:
/**
* Get the type of the notification being broadcast.
*/
public function broadcastType(): string
{
return 'broadcast.message';
}
Listening for Notifications
Notifications will broadcast on a private channel
formatted using a {notifiable}.{id}
convention. So, if you are sending a notification to an
App\Models\User instance with an ID of
1, the notification will be broadcast on
the App.Models.User.1 private channel. When
using Laravel
Echo, you may easily listen for notifications on
a channel using the notification
method:
Echo.private('App.Models.User.' userId)
.notification((notification) => {
console.log(notification.type);
});
Customizing the Notification Channel
If you would like to customize which channel that an
entity's broadcast notifications are broadcast on, you
may define a
receivesBroadcastNotificationsOn method on
the notifiable entity:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Broadcasting\PrivateChannel;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable;
class User extends Authenticatable
{
use Notifiable;
/**
* The channels the user receives notification broadcasts on.
*/
public function receivesBroadcastNotificationsOn(): string
{
return 'users.'.$this->id;
}
}
SMS Notifications
Prerequisites
Sending SMS notifications in Laravel is powered by Vonage (formerly
known as Nexmo). Before you can send notifications via
Vonage, you need to install the
laravel/vonage-notification-channel and
guzzlehttp/guzzle packages:
composer require laravel/vonage-notification-channel guzzlehttp/guzzle
The package includes a configuration
file. However, you are not required to export
this configuration file to your own application. You can
simply use the VONAGE_KEY and
VONAGE_SECRET environment variables to
define your Vonage public and secret keys.
After defining your keys, you should set a
VONAGE_SMS_FROM environment variable that
defines the phone number that your SMS messages should
be sent from by default. You may generate this phone
number within the Vonage control panel:
VONAGE_SMS_FROM=15556666666
Formatting SMS Notifications
If a notification supports being sent as an SMS, you
should define a toVonage method on the
notification class. This method will receive a
$notifiable entity and should return an
Illuminate\Notifications\Messages\VonageMessage
instance:
use Illuminate\Notifications\Messages\VonageMessage;
/**
* Get the Vonage / SMS representation of the notification.
*/
public function toVonage(object $notifiable): VonageMessage
{
return (new VonageMessage)
->content('Your SMS message content');
}
Unicode Content
If your SMS message will contain unicode characters, you
should call the unicode method when
constructing the VonageMessage
instance:
use Illuminate\Notifications\Messages\VonageMessage;
/**
* Get the Vonage / SMS representation of the notification.
*/
public function toVonage(object $notifiable): VonageMessage
{
return (new VonageMessage)
->content('Your unicode message')
->unicode();
}
Customizing the "From" Number
If you would like to send some notifications from a phone
number that is different from the phone number specified
by your VONAGE_SMS_FROM environment
variable, you may call the from method on a
VonageMessage instance:
use Illuminate\Notifications\Messages\VonageMessage;
/**
* Get the Vonage / SMS representation of the notification.
*/
public function toVonage(object $notifiable): VonageMessage
{
return (new VonageMessage)
->content('Your SMS message content')
->from('15554443333');
}
Adding a Client Reference
If you would like to keep track of costs per user, team, or client, you may add a "client reference" to the notification. Vonage will allow you to generate reports using this client reference so that you can better understand a particular customer's SMS usage. The client reference can be any string up to 40 characters:
use Illuminate\Notifications\Messages\VonageMessage;
/**
* Get the Vonage / SMS representation of the notification.
*/
public function toVonage(object $notifiable): VonageMessage
{
return (new VonageMessage)
->clientReference((string) $notifiable->id)
->content('Your SMS message content');
}
Routing SMS Notifications
To route Vonage notifications to the proper phone number,
define a routeNotificationForVonage method
on your notifiable entity:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
class User extends Authenticatable
{
use Notifiable;
/**
* Route notifications for the Vonage channel.
*/
public function routeNotificationForVonage(Notification $notification): string
{
return $this->phone_number;
}
}
Slack Notifications
Prerequisites
Before sending Slack notifications, you should install the Slack notification channel via Composer:
composer require laravel/slack-notification-channel
Additionally, you must create a Slack App for your Slack workspace.
If you only need to send notifications to the same Slack
workspace that the App is created in, you should ensure
that your App has the chat:write,
chat:write.public, and
chat:write.customize scopes. These scopes
can be added from the "OAuth &
Permissions" App management tab within Slack.
Next, copy the App's "Bot User OAuth Token" and
place it within a slack configuration array
in your application's services.php
configuration file. This token can be found on the
"OAuth & Permissions" tab within
Slack:
'slack' => [
'notifications' => [
'bot_user_oauth_token' => env('SLACK_BOT_USER_OAUTH_TOKEN'),
'channel' => env('SLACK_BOT_USER_DEFAULT_CHANNEL'),
],
],
App Distribution
If your application will be sending notifications to external Slack workspaces that are owned by your application's users, you will need to "distribute" your App via Slack. App distribution can be managed from your App's "Manage Distribution" tab within Slack. Once your App has been distributed, you may use Socialite to obtain Slack Bot tokens on behalf of your application's users.
Formatting Slack Notifications
If a notification supports being sent as a Slack message,
you should define a toSlack method on the
notification class. This method will receive a
$notifiable entity and should return an
Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\SlackMessage
instance. You can construct rich notifications using Slack's Block
Kit API. The following example may be previewed
in Slack's
Block Kit builder:
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Blocks\ContextBlock;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Blocks\SectionBlock;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Composites\ConfirmObject;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\SlackMessage;
/**
* Get the Slack representation of the notification.
*/
public function toSlack(object $notifiable): SlackMessage
{
return (new SlackMessage)
->text('One of your invoices has been paid!')
->headerBlock('Invoice Paid')
->contextBlock(function (ContextBlock $block) {
$block->text('Customer #1234');
})
->sectionBlock(function (SectionBlock $block) {
$block->text('An invoice has been paid.');
$block->field("*Invoice No:*\n1000")->markdown();
$block->field("*Invoice Recipient:*\ntaylor@laravel.com")->markdown();
})
->dividerBlock()
->sectionBlock(function (SectionBlock $block) {
$block->text('Congratulations!');
});
}
Slack Interactivity
Slack's Block Kit notification system provides powerful features to handle user interaction. To utilize these features, your Slack App should have "Interactivity" enabled and a "Request URL" configured that points to a URL served by your application. These settings can be managed from the "Interactivity & Shortcuts" App management tab within Slack.
In the following example, which utilizes the
actionsBlock method, Slack will send a
POST request to your "Request
URL" with a payload containing the Slack user who
clicked the button, the ID of the clicked button, and
more. Your application can then determine the action to
take based on the payload. You should also verify
the request was made by Slack:
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Blocks\ActionsBlock;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Blocks\ContextBlock;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Blocks\SectionBlock;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\SlackMessage;
/**
* Get the Slack representation of the notification.
*/
public function toSlack(object $notifiable): SlackMessage
{
return (new SlackMessage)
->text('One of your invoices has been paid!')
->headerBlock('Invoice Paid')
->contextBlock(function (ContextBlock $block) {
$block->text('Customer #1234');
})
->sectionBlock(function (SectionBlock $block) {
$block->text('An invoice has been paid.');
})
->actionsBlock(function (ActionsBlock $block) {
// ID defaults to "button_acknowledge_invoice"...
$block->button('Acknowledge Invoice')->primary();
// Manually configure the ID...
$block->button('Deny')->danger()->id('deny_invoice');
});
}
Confirmation Modals
If you would like users to be required to confirm an
action before it is performed, you may invoke the
confirm method when defining your button.
The confirm method accepts a message and a
closure which receives a ConfirmObject
instance:
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Blocks\ActionsBlock;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Blocks\ContextBlock;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Blocks\SectionBlock;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\BlockKit\Composites\ConfirmObject;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\SlackMessage;
/**
* Get the Slack representation of the notification.
*/
public function toSlack(object $notifiable): SlackMessage
{
return (new SlackMessage)
->text('One of your invoices has been paid!')
->headerBlock('Invoice Paid')
->contextBlock(function (ContextBlock $block) {
$block->text('Customer #1234');
})
->sectionBlock(function (SectionBlock $block) {
$block->text('An invoice has been paid.');
})
->actionsBlock(function (ActionsBlock $block) {
$block->button('Acknowledge Invoice')
->primary()
->confirm(
'Acknowledge the payment and send a thank you email?',
function (ConfirmObject $dialog) {
$dialog->confirm('Yes');
$dialog->deny('No');
}
);
});
}
Inspecting Slack Blocks
If you would like to quickly inspect the blocks you've
been building, you can invoke the dd method
on the SlackMessage instance. The
dd method will generate and dump a URL to
Slack's Block
Kit Builder, which displays a preview of the
payload and notification in your browser. You may pass
true to the dd method to dump
the raw payload:
return (new SlackMessage)
->text('One of your invoices has been paid!')
->headerBlock('Invoice Paid')
->dd();
Routing Slack Notifications
To direct Slack notifications to the appropriate Slack
team and channel, define a
routeNotificationForSlack method on your
notifiable model. This method can return one of three
values:
null- which defers routing to the channel configured in the notification itself. You may use thetomethod when building yourSlackMessageto configure the channel within the notification.- A string specifying the Slack channel to send the
notification to, e.g.
#support-channel. - A
SlackRouteinstance, which allows you to specify an OAuth token and channel name, e.g.SlackRoute::make($this->slack_channel, $this->slack_token). This method should be used to send notifications to external workspaces.
For instance, returning #support-channel
from the routeNotificationForSlack method
will send the notification to the
#support-channel channel in the workspace
associated with the Bot User OAuth token located in your
application's services.php configuration
file:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
class User extends Authenticatable
{
use Notifiable;
/**
* Route notifications for the Slack channel.
*/
public function routeNotificationForSlack(Notification $notification): mixed
{
return '#support-channel';
}
}
Notifying External Slack Workspaces
Note:
Before sending notifications to external Slack workspaces, your Slack App must be distributed.
Of course, you will often want to send notifications to the Slack workspaces owned by your application's users. To do so, you will first need to obtain a Slack OAuth token for the user. Thankfully, Laravel Socialite includes a Slack driver that will allow you to easily authenticate your application's users with Slack and obtain a bot token.
Once you have obtained the bot token and stored it within
your application's database, you may utilize the
SlackRoute::make method to route a
notification to the user's workspace. In addition, your
application will likely need to offer an opportunity for
the user to specify which channel notifications should
be sent to:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Slack\SlackRoute;
class User extends Authenticatable
{
use Notifiable;
/**
* Route notifications for the Slack channel.
*/
public function routeNotificationForSlack(Notification $notification): mixed
{
return SlackRoute::make($this->slack_channel, $this->slack_token);
}
}
Localizing Notifications
Laravel allows you to send notifications in a locale other than the HTTP request's current locale, and will even remember this locale if the notification is queued.
To accomplish this, the
Illuminate\Notifications\Notification class
offers a locale method to set the desired
language. The application will change into this locale
when the notification is being evaluated and then revert
back to the previous locale when evaluation is
complete:
$user->notify((new InvoicePaid($invoice))->locale('es'));
Localization of multiple notifiable entries may also be
achieved via the Notification facade:
Notification::locale('es')->send(
$users, new InvoicePaid($invoice)
);
User Preferred Locales
Sometimes, applications store each user's preferred
locale. By implementing the
HasLocalePreference contract on your
notifiable model, you may instruct Laravel to use this
stored locale when sending a notification:
use Illuminate\Contracts\Translation\HasLocalePreference;
class User extends Model implements HasLocalePreference
{
/**
* Get the user's preferred locale.
*/
public function preferredLocale(): string
{
return $this->locale;
}
}
Once you have implemented the interface, Laravel will
automatically use the preferred locale when sending
notifications and mailables to the model. Therefore,
there is no need to call the locale method
when using this interface:
$user->notify(new InvoicePaid($invoice));
Testing
You may use the Notification facade's
fake method to prevent notifications from
being sent. Typically, sending notifications is
unrelated to the code you are actually testing. Most
likely, it is sufficient to simply assert that Laravel
was instructed to send a given notification.
After calling the Notification facade's
fake method, you may then assert that
notifications were instructed to be sent to users and
even inspect the data the notifications received:
<?php
namespace Tests\Feature;
use App\Notifications\OrderShipped;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Notification;
use Tests\TestCase;
class ExampleTest extends TestCase
{
public function test_orders_can_be_shipped(): void
{
Notification::fake();
// Perform order shipping...
// Assert that no notifications were sent...
Notification::assertNothingSent();
// Assert a notification was sent to the given users...
Notification::assertSentTo(
[$user], OrderShipped::class
);
// Assert a notification was not sent...
Notification::assertNotSentTo(
[$user], AnotherNotification::class
);
// Assert that a given number of notifications were sent...
Notification::assertCount(3);
}
}
You may pass a closure to the assertSentTo
or assertNotSentTo methods in order to
assert that a notification was sent that passes a given
"truth test". If at least one notification was
sent that passes the given truth test then the assertion
will be successful:
Notification::assertSentTo(
$user,
function (OrderShipped $notification, array $channels) use ($order) {
return $notification->order->id === $order->id;
}
);
On-Demand Notifications
If the code you are testing sends on-demand
notifications, you can test that the on-demand
notification was sent via the
assertSentOnDemand method:
Notification::assertSentOnDemand(OrderShipped::class);
By passing a closure as the second argument to the
assertSentOnDemand method, you may
determine if an on-demand notification was sent to the
correct "route" address:
Notification::assertSentOnDemand(
OrderShipped::class,
function (OrderShipped $notification, array $channels, object $notifiable) use ($user) {
return $notifiable->routes['mail'] === $user->email;
}
);
Notification Events
Notification Sending Event
When a notification is sending, the
Illuminate\Notifications\Events\NotificationSending
event is dispatched by the
notification system. This contains the
"notifiable" entity and the notification
instance itself. You may register listeners for this
event in your application's
EventServiceProvider:
use App\Listeners\CheckNotificationStatus;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Events\NotificationSending;
/**
* The event listener mappings for the application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $listen = [
NotificationSending::class => [
CheckNotificationStatus::class,
],
];
The notification will not be sent if an event listener
for the NotificationSending event returns
false from its handle
method:
use Illuminate\Notifications\Events\NotificationSending;
/**
* Handle the event.
*/
public function handle(NotificationSending $event): bool
{
return false;
}
Within an event listener, you may access the
notifiable, notification, and
channel properties on the event to learn
more about the notification recipient or the
notification itself:
/**
* Handle the event.
*/
public function handle(NotificationSending $event): void
{
// $event->channel
// $event->notifiable
// $event->notification
}
Notification Sent Event
When a notification is sent, the
Illuminate\Notifications\Events\NotificationSent
event is dispatched by the
notification system. This contains the
"notifiable" entity and the notification
instance itself. You may register listeners for this
event in your EventServiceProvider:
use App\Listeners\LogNotification;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Events\NotificationSent;
/**
* The event listener mappings for the application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $listen = [
NotificationSent::class => [
LogNotification::class,
],
];
Note:
After registering listeners in yourEventServiceProvider, use theevent:generateArtisan command to quickly generate listener classes.
Within an event listener, you may access the
notifiable, notification,
channel, and response
properties on the event to learn more about the
notification recipient or the notification itself:
/**
* Handle the event.
*/
public function handle(NotificationSent $event): void
{
// $event->channel
// $event->notifiable
// $event->notification
// $event->response
}
Custom Channels
Laravel ships with a handful of notification channels,
but you may want to write your own drivers to deliver
notifications via other channels. Laravel makes it
simple. To get started, define a class that contains a
send method. The method should receive two
arguments: a $notifiable and a
$notification.
Within the send method, you may call methods
on the notification to retrieve a message object
understood by your channel and then send the
notification to the $notifiable instance
however you wish:
<?php
namespace App\Notifications;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
class VoiceChannel
{
/**
* Send the given notification.
*/
public function send(object $notifiable, Notification $notification): void
{
$message = $notification->toVoice($notifiable);
// Send notification to the $notifiable instance...
}
}
Once your notification channel class has been defined,
you may return the class name from the via
method of any of your notifications. In this example,
the toVoice method of your notification can
return whatever object you choose to represent voice
messages. For example, you might define your own
VoiceMessage class to represent these
messages:
<?php
namespace App\Notifications;
use App\Notifications\Messages\VoiceMessage;
use App\Notifications\VoiceChannel;
use Illuminate\Bus\Queueable;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\ShouldQueue;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notification;
class InvoicePaid extends Notification
{
use Queueable;
/**
* Get the notification channels.
*/
public function via(object $notifiable): string
{
return VoiceChannel::class;
}
/**
* Get the voice representation of the notification.
*/
public function toVoice(object $notifiable): VoiceMessage
{
// ...
}
}